To en 1997 en 1997 1 7 4 1 p states that the design of piles shall be based on one of the following approaches.
Lateral load from friction piles on steel sheeting.
The basic specification for steel sheet piling in the united states has been astm a 328 published by the american society of testing materials.
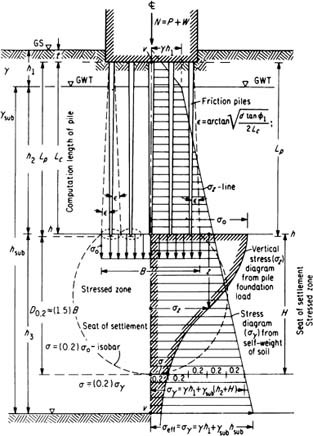
1 the soil above the neutral plane does not contribute to side resistance.
Flat sheet ps piling products.
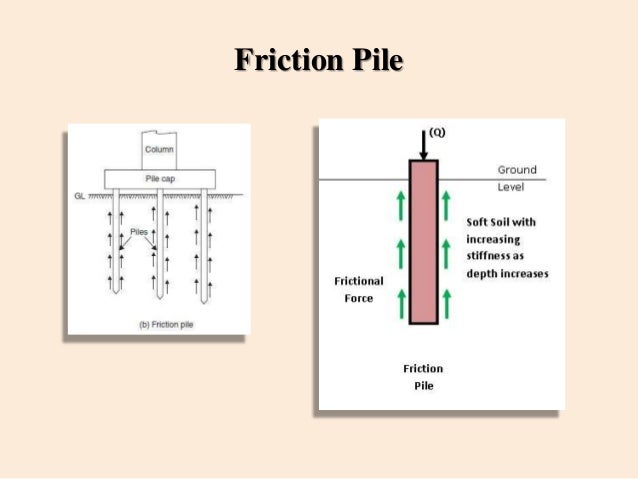
Friction pile is a kind of pile foundation.
The ultimate lateral resistance of the loose sand layer depends on the friction angle and effective overburden stress.
This grade has been satisfactory for most applications in that it provided a relatively high yield point for design and a high ultimate strength for drivability.
The load capacity is a function of the reduction factor α.
Depending on soil layers.
The behavior of short rigid piles under lateral loads is discussed later in this chapter.
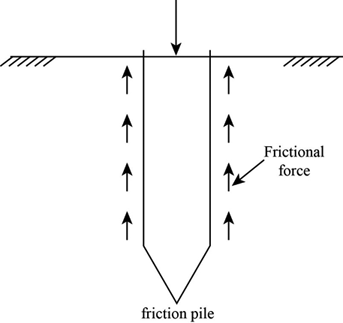
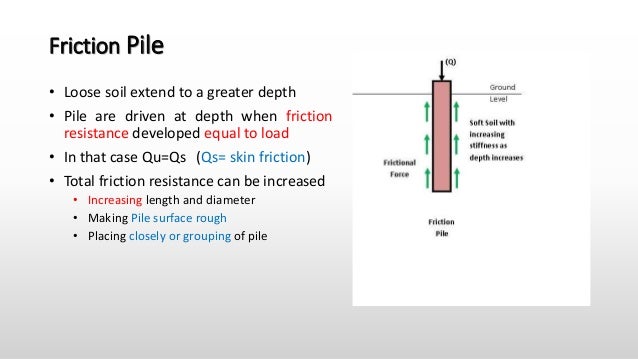
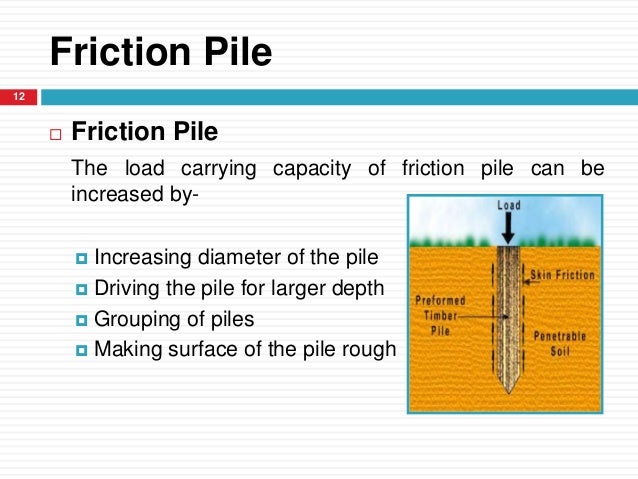
Friction can be developed for the entire length of the pile or a definite length of the pile depending on the strata of the soil.
Z piles are commonly used for cantilevered tied back king pile and combi wall retaining systems.
This example highlights the effects of downdrag on pile design.
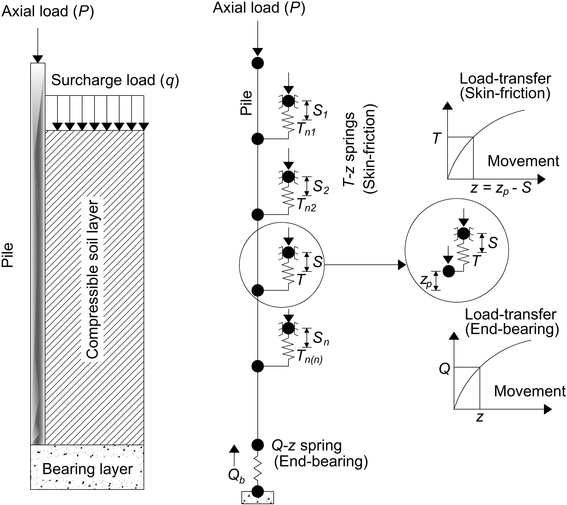
Typical load settlement curves for compressive load tests.
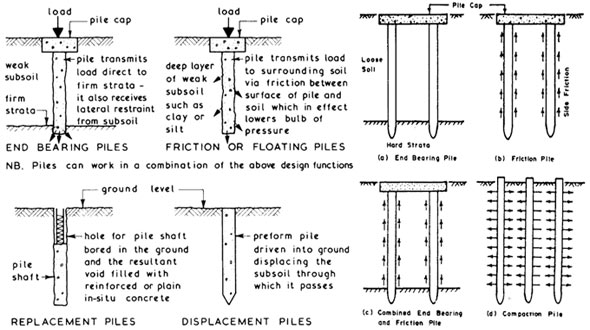
This type of pile utilizes the frictional resistance force between the pile surface and adjacent soil to transfer the superstructure load.
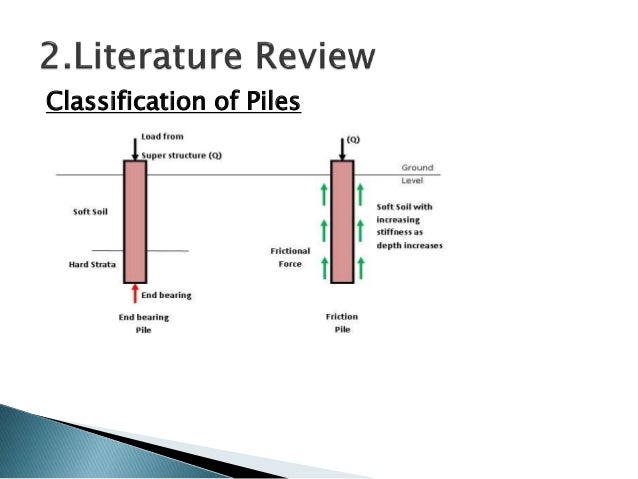
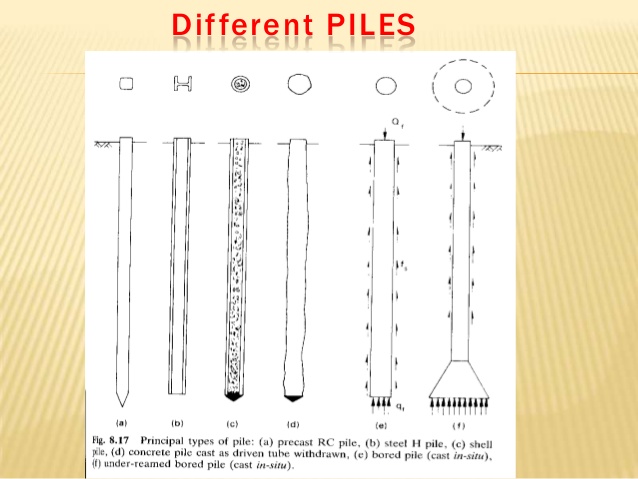
Friction piles cohesion piles combination of friction and cohesion piles 1 4 2 end bearing piles these piles transfer their load on to a firm stratum located at a considerable depth below the base of the structure and they derive most of their carrying capacity from the penetration resistance of the soil at the toe of the pile see figure 1 1.
A for friction pile and b for end bearing pile.
Lateral forces on embedded piles may produce high bending stresses and deflections.
Depending on the subsoil strata condition resistance force due to friction can develop in a definite pile length of on the full length.
Friction pile transfers the load from the structure to the soil by the frictional force between the surface of the pile and the soil surrounding the pile such as stiff clay sandy soil etc.
Piles in clays or cohesive soils carry most of the load by skin friction resistance of the pile shaft.
This example also demonstrates how prebored holes can be used to relieve part of the downdrag load.
Approaches of pile design acc.
2 downward relative movement of soil above the neutral plane exerts drag load to the pile.
The load carrying capacity using static formula is computed on the basis of total stress approach taking ɸ u 0 assuming undrained conditions.
Grades of sheet piling steel.
Additional applications also include load bearing bridge abutments.
They are typically used for circular cell design.