Interstitial condensation is a form of damp that occurs when warm moist air from inside a structure moves into a wall and reaches the dew point and condenses within the core of the wall to form water.
Interstitial condensation warm roof.
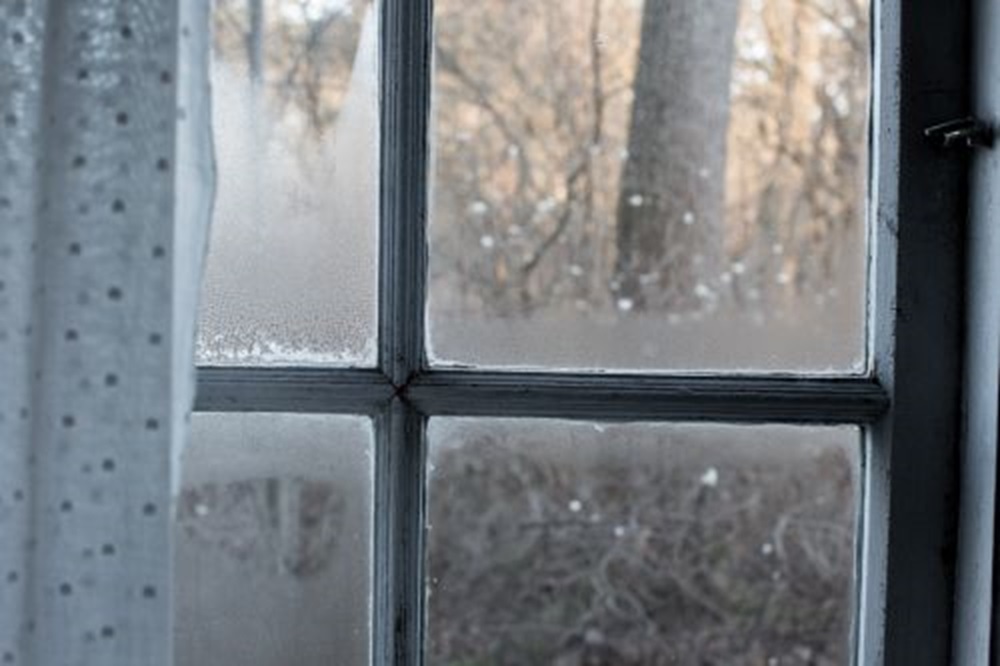
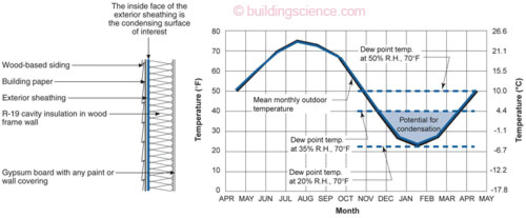
Condensation can occur in heated buildingswhen water vapour usually produced by the occupants and their activities condenses on exposed buildingsurfaces surface condensation where it supports mould growth or within buildingelements interstitial condensation.
Inside the roof wall or floor elements.
Interstitial condensation can cause deterioration or even failure of the components of the assembly potentially shortening their useful lifespan.
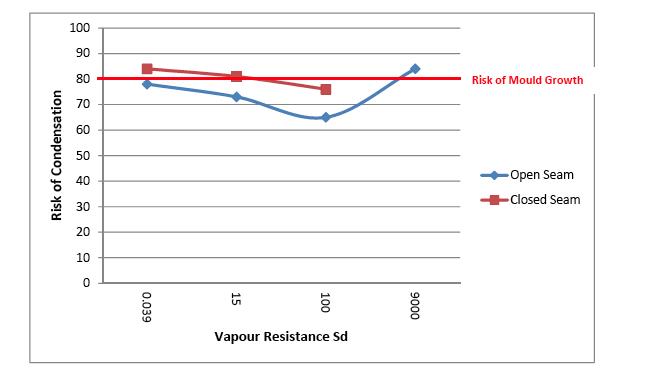
Condensation risk analysis cra.
Interstitial condensation commonly occurs when moist air permeates through elements of the building fabric across which there is a temperature difference typically but not always when warm moist internal air moves towards the cooler outer parts of external walls or roofs driven by a pressure difference.
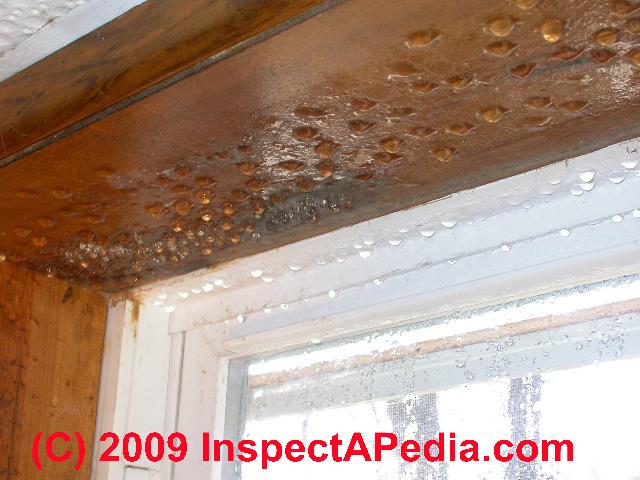
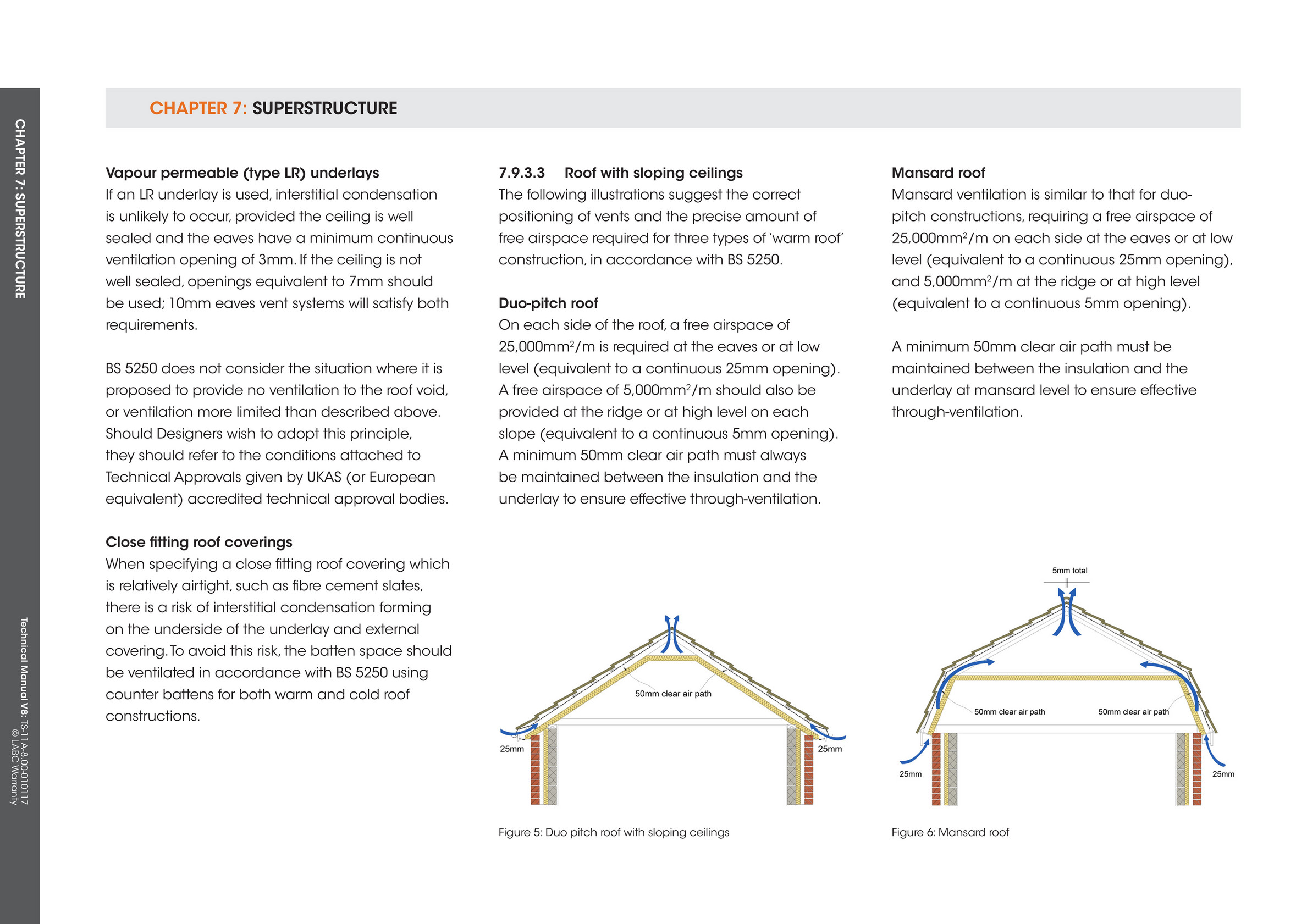
Interstitial condensation is a particular problem in cold deck roofs where the insulation is placed in between the joists in the void above the ceiling.
Inside the roof wall or floor elements.
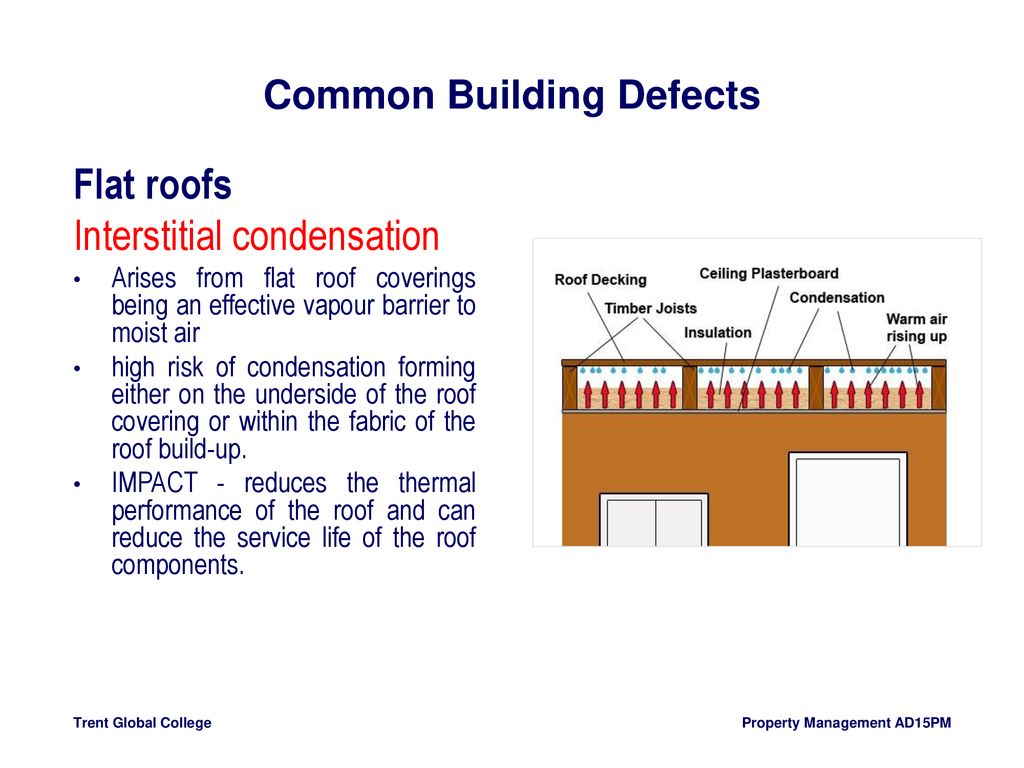
Interstitial condensation can create structural dampening that occurs when moist air penetrates inside the hidden space within an enclosed wall roof or floor cavity structure.
Interstitial condensation can penetrate the walls floors and ceilings of a structure.
It is important to ensure an element is designed to avoid interstitial condensation or to create an adequate ventilation solution to remove any condensation that forms.
Let us use roof timbers as an example.
Interstitial condensation is a form of structural damp that occurs when warm moist air penetrates inside a wall roof or floor structure.
Interstitial condensation is condensation which occurs between layers of the construction i e.
Interstitial condensation is condensation which occurs between layers of the construction i e.
Upon contact the warm air cools reaches its dew point and forms water droplets on the outside of the.
When that moisture laden air reaches a layer inside the interstitial structure that is at dew point temperature it condenses into liquid water on that surface.
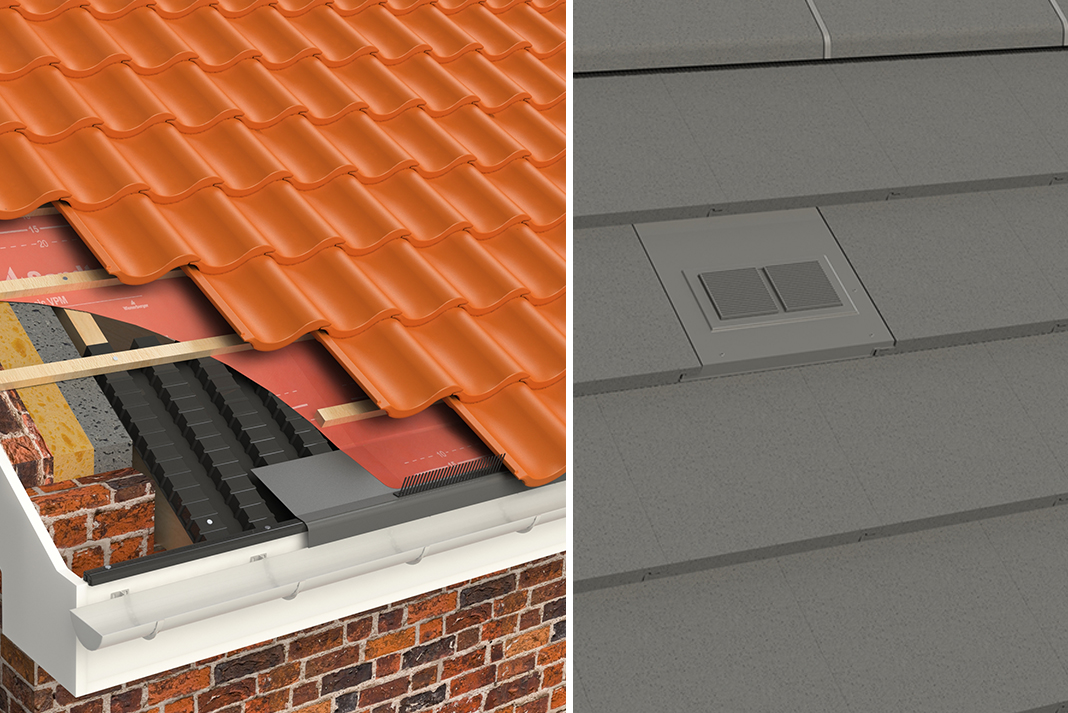
The incorporation of adequate insulation and ventilation in the roof void of a cold roof construction or sufficient insulation and vapour control layer in a warm roof construction will prevent the formation of interstitial condensation in the normal range of environmental conditions experienced.
Interstitial condensation can cause deterioration or even failure of the components of the assembly potentially shortening their useful lifespan.
Interstitial condensation happens on the inside of a structural material whereas condensation happens on the outside.
The standard of roof ventilation varies widely but the current building regulations specify that 270mm mineral wool should be used to insulate your a roof space at a minimum.











.png?width=400&ext=.jpg)